We’re excited to announce Geolocation and Geofencing support for our MIDAS room and resource scheduling software.
What is Geolocation?

Geolocation is the process of determining the geographic location of a user’s device. It is used in a variety of applications, such as mapping, navigation, and weather forecasting. A device’s location can be determined using a variety of methods, including GPS, cell tower triangulation, and IP address location.
IP address geolocation is a method of determining the position in the world of an IP address. This can be done by using a variety of methods, including:
- Reverse DNS lookup: This method involves looking up the IP address in a DNS database to determine the name of the domain that is associated with the IP address. The domain name can then be used to determine the geographic location of the server that hosts the domain.
- Geolocation databases: These databases contain information about the geographic location of IP addresses. This information is typically collected from a variety of sources, such as ISPs and network operators.
It is important to note that IP address geolocation is not always accurate. The accuracy of IP address geolocation depends on a variety of factors. These include the quality of the geolocation database and the method that is used to determine the geographic location of the IP address.
What is Geofencing?
Geofencing is an extension of geolocation. Once a device’s geographic location can be determined through geolocation, “Geofencing” can be used by a website or application to ensure that devices outside of an authorized area are denied access.
IP geofencing works by creating a virtual radius at a set distance around a fixed point on the globe. By comparing the latitude and longitude coordinates of a user’s device, with this fixed point, the distance between them can be calculated. This calculation will determine whether the user’s device falls within the set virtual radius.
Access form any device which falls outside of a set radius of the central fixed location can then be blocked.
Geolocation applications within MIDAS
Initially, there are two main areas within our booking software where geolocation information can be shown.
First, is the Recent Activity Log. This audit log in MIDAS records all user activity and actions taking place in your booking system. Each entry in the log is time-stamped, and shows the user account and IP address which performed the action.
From MIDAS v4.33, the optional Geolocation addon can be configured to allow location information to be shown for IP addresses in the Recent Activity Log. This location information includes the city, region, and country that the IP address resides in.
The second application for geolocation in MIDAS accompanies the unfamiliar login notifications feature.
The unfamiliar login notifications feature alerts users when their account is signed in to from a new device or location.
These notifications typically include details of the user’s device / browser and their IP address.
Geolocation support now means that you can optionally configure these notifications to now also include the city, region, and country that the login occurred from.
Geofencing applications within MIDAS
Building on the new geolocation support, Geofencing can be used to further enhance the security of your MIDAS system.
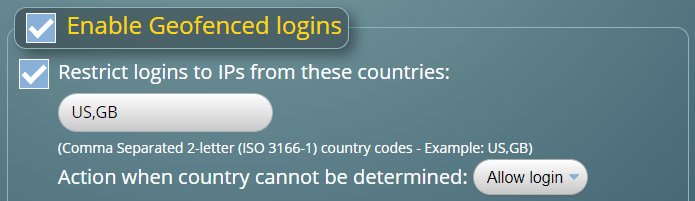
It can be used to restrict account logins to certain countries. For example, if your organization only has offices within the United States and the United Kingdom, your colleagues are typically likely to only need to login to MIDAS from within either the US or the UK. You can use geofencing to block any login attempts originating from countries other than the US or the UK.
Geofencing can additionally (or alternatively) also restrict account logins to within a certain distance from your location. For example, if you run a radio station in Manchester, UK, you could restrict logins to your MIDAS system to within say a 10 mile radius of Manchester.

How to enable Geolocation or Geofencing in MIDAS
The new Geolocation and Geofencing features are available for MIDAS v4.33 (or later) via our optional Geolocation addon.
Existing customers with active subscriptions can obtain this addon via mid.as/upgrade.
If you’re new to MIDAS, you can subscribe with the Geolocation addon via mid.as/pricing.
Geolocation data accuracy
The accuracy of IP geolocation data depends on a number of factors, including the quality and freshness of the geolocation database, the method that is used to determine the geographic location of the IP address, and the type of IP address.
The IP geolocation data we use in the Geolocation addon for MIDAS is never more than 30 days old.
In general, IP geolocation data is most accurate for large geographic areas, such as countries or states. It can become less accurate for smaller geographic areas, such as cities or neighborhoods.
That’s why if you use the distance based geofence features of the Geolocation addon, you should always set a larger liberal distance than necessary, rather than a very small strict distance from your location. The Geolocation addon does include an instant IP lookup test tool, so you can check IP distances before you apply them.
The Geolocation addon also includes “fallback” options for both country / distance geofence enforcement. For IP addresses where a country and/or latitude and longitude coordinates cannot be determined, you can configure MIDAS to either block or allow these connections.
It’s also worth noting that the accuracy of IP geolocation data can be affected by the use of proxy servers and VPNs. Proxy servers and VPNs can mask the true IP address of a device, making it difficult to determine the device’s geographic location.