
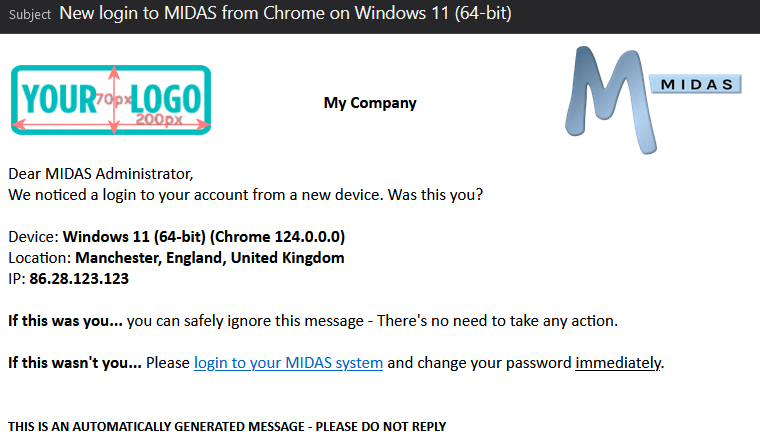
Whenever your user account is logged into from a new or unfamiliar device, MIDAS can automatically alert you by email. This additional security feature helps keep your account secure by alerting you to suspicious logins. An unfamiliar login notification includes details of the browser, operating system, IP address, and – with our optional Geolocation addon – location, of the device that’s just logged into your account.
Until now, MIDAS has been unable to distinguish between more recent operating system versions. For example, between Windows 10 and Windows 11, or between MacOS Ventura and Sonoma.
This is because MIDAS has relied on the “User Agent” (UA) string that’s presented by the browser that’s logging in.
Here’s an example of a browser’s “User Agent” string presented to a web server:
Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/123.0.0.0 Safari/537.36
There’s a lot of information there, but essentially, from this string MIDAS can derive that it’s a Windows (64 bit) device, and the browser is Google Chrome 123.
Here’s another example:
Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10.15; rv:124.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/124.0
From this, MIDAS can derive that it’s a macOS device, and the browser is Firefox 124.
But wait… can’t MIDAS also determine the exact version of the operating system from these UA strings?
Mac OS X 10.15…. Catalina? …Big Sur? …Monterey? …Ventura?
Doesn’t “Mac OS X 10.15” imply macOS Catalina? ..and doesn’t “Windows NT 10.0” imply Windows 10?
Well, that used to be the case, but not any more!
Modern browsers now “clamp” the versions of more recent macOS/Windows operating systems reported by the User Agent string. For macOS operating systems, the User Agent string will report a maximum of macOS X 10.15. For Windows operating systems, a maximum of Windows 10 will be reported. Browsers no longer natively report the specific version of the operating system they’re running on.
This means that a Chrome browser running on either Windows 10 or Windows 11 will report “Windows NT 10.0”. Similarly, macOS Catalina (10.15), Big Sur (11), Monterey (12), Ventura (13), and Sonoma (14), will all report “Mac OS X 10.15”.
So Windows 10 and 11 are the same then?
In an effort to improve user privacy, browsers have decided to no longer reveal the specific operating system version a user is using when visiting a website, in order to make it harder for websites to “fingerprint” users.
“Fingerprinting” is a technique that some websites employ to uniquely identify and potentially track visitors.
So because of these changes to the way browsers report User Agent strings, it’s been difficult for MIDAS to provide a unfamiliar login notification containing details of exact operating system version that’s been used to login to an account.
But advancements in technology mean that we’ve now been able to make improvements to device detection for MIDAS v4.36.
Utilizing New “Client Hint” technology
Client hints are a set of HTTP request headers that provide useful information about the client such as device type and network conditions. This then allow servers to optimize what is served for those conditions.
Unlike the traditional “User Agent String”, client hints provide a more efficient and privacy preserving way of getting the desired information.
A web server can proactively request the client hint headers they are interested in. The browser can then include the requested headers in subsequent requests.
If the web server upon which a MIDAS system is running proactively requests either the “sec-ch-ua-platform-version” or “ua-platform-version” client hint header, MIDAS can receive details of the user’s operating system version.
Unfamiliar login notifications (if enabled) can then provide much more accurate information as to the operating system of the new device which has logged into your account.
Web Server Configuration
Because a web server has to proactively request these new client headers in order for browsers to respond to them, servers have to be configured accordingly.
All of our cloud-hosted nodes have been appropriately configured. Our client servers now proactively request the necessary Client Hint headers. This in turn means that all cloud hosted users can start to take advantage of these improvements to device detection and unfamiliar login notifications.
For self-hosted customers, a small configuration change to the web server when your MIDAS system is running from is required.
Details of the configuration change you’ll need to make can be found in our KB article, How to configure your server for Client Hints.